Lab 1: Use of DMM, Power Supplies (CC/CV), Batteries
Objectives
- Practice the use of digital multimeter (DMM) to measure voltage.
- Understand the operation and limitation of power supplies in constant current (CC) and constant voltage (CV) modes.
- Understand lithium-ion polymer battery characteristics, including charging and discharging methodologies.
Introduction
Lithium-ion polymer batteries are (currently, as of 2023) commonly used in portable devices (such as phones, laptops, etc.) for more than decade. Therefore, knowing their characteristics is an important basic toward advanced applications. Examples include protection circuits, electric vehicles, battery backup solutions, and solar panel energy storage solutions.
Moreover, this laboratory will introduce a technique called “shunt resistor” to measure the current flowing through a system by measuring voltage drop across a small-value, or shunt, resistor without having to connect an ammeter across the current-flowing path. This technique is extremely useful, especially in case of continuous current supply with limited tools, because the devices does not need to be disconnected to measure the flowing current.
Apparatus
- Resistors: 0.1Ω and 50Ω
- Lithium-ion Polymer Battery
- Programmable DC Power Supply
- Digital Multimeter
- Breadboard
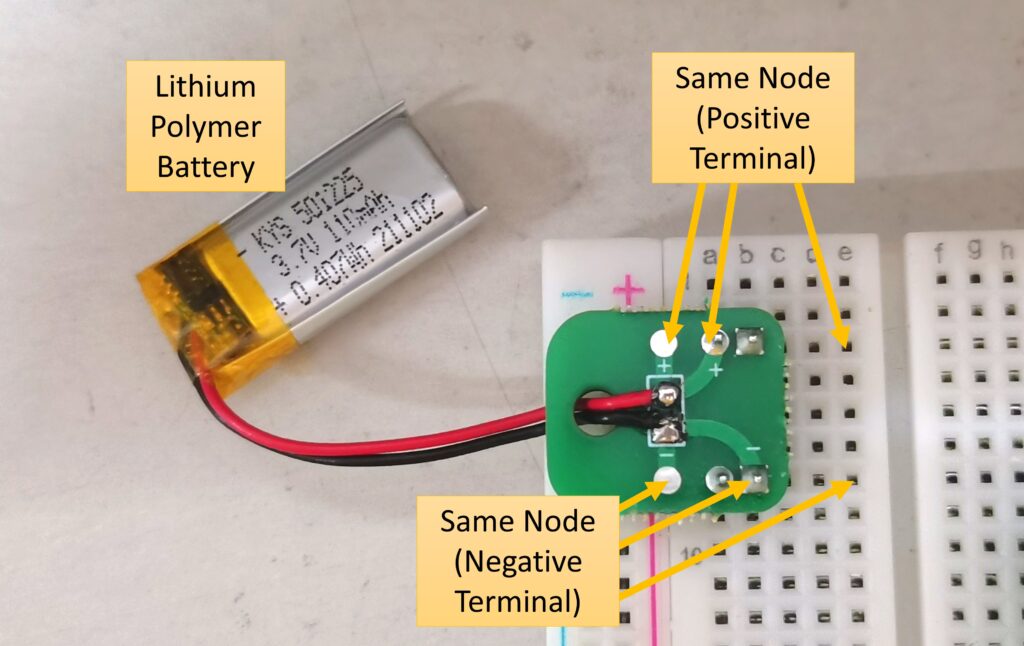
Methodology
This laboratory will explore the characteristics of lithium-ion polymer battery. We will first try to charge the battery to 4.2 volt for 1 hour (Figure 2a), then discharge them using a 50-ohm resistor for another hour (Figure 2b). The current measurements will be taken from the shunt resistor ![]() .
.
The charging or discharging current is usually determined by a constant
, which is equals to battery capacity in
or
, divided by 1 hour. In this case, our battery has a capacity of
, so
. Therefore, if we charge at 55mA, we can say that we are charging at 0.5C.

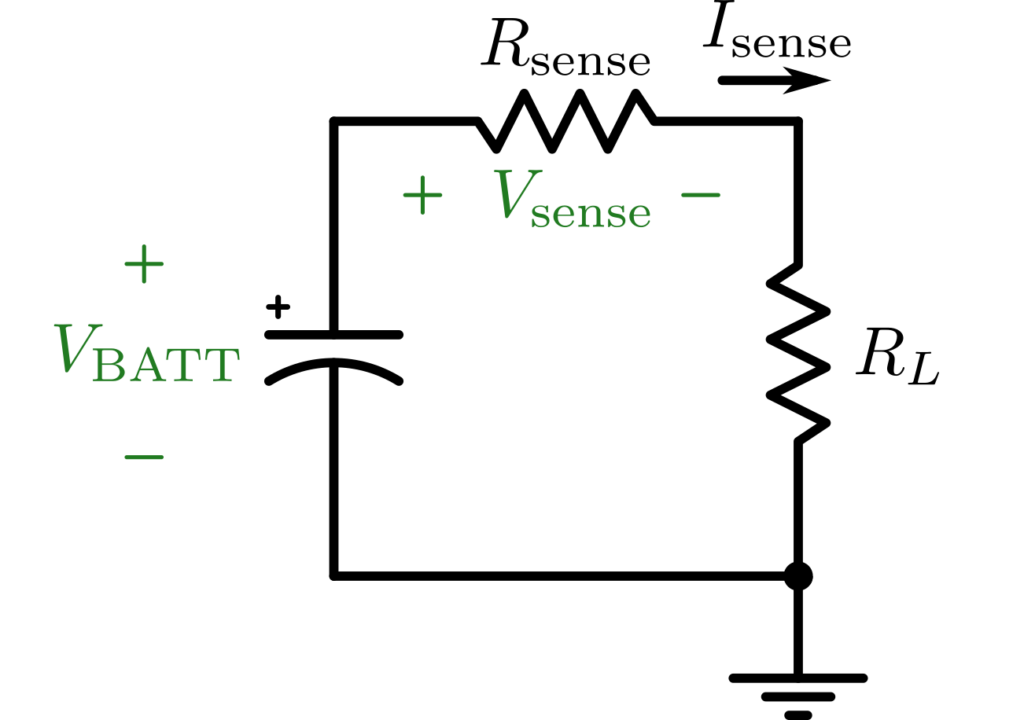
Procedures
Measure the Resistances
Use the multimeter in resistance measurement mode to measure the values of 0.1Ω and 50Ω resistors. Note down the actual values. Calculate the percentage error.
Measure the Initial Voltage of Lithium-ion Polymer Battery
Insert the battery on top of the breadboard. Use the multimeter in voltage mode to measure the voltage of battery. The nominal voltage of lithium-ion polymer batteries is 3.7V. Values higher than this means that the battery has been charged to some extent.
Charge the Battery
Refer to Figure 2a.
- Set the DC power source
 to be 4.2V and 80mA (or 0.08A). Do not connect the wires yet.
to be 4.2V and 80mA (or 0.08A). Do not connect the wires yet. - Connect the circuit according to Figure 2a, with
 .
. - Let one of the TAs or the instructor inspect your circuit, then turn on the channel and connect the wires to power supply.
- Record the voltages of
 and
and  , including power supply mode for 1 hour.
, including power supply mode for 1 hour.
Swapping the positive and negative terminals can create a short-circuit and leads to fire!
Notice that the power supply first acts as constant current supply with rising voltage, then it changes to constant voltage supply with dropping current.
Discharge the Battery
Refer to Figure 2b.
- Remove the DC power source and record the battery voltage.
- Connect
 instead of the DC power supply.
instead of the DC power supply. - Record the voltages of
 and
and  for 1 hour.
for 1 hour.
Do not connect 0.1Ω resistor directly to the battery, as we can create a short-circuit and leads to fire! Double-check the values!
Lab Worksheet
Complete the lab worksheet and submit by Monday.
Further Readings
- What is Lithium Polymer Battery ?, DNK Power – A good summary of lithium-ion polymer batteries concepts.
- A review of lithium-ion battery safety concerns: The issues, strategies, and testing standards – A paper with good introduction toward lithium-ion based batteries construction and safety concerns.
- Shunt Resistors <Current Sense Shunt Resistors> – a great explanation of shunt resistor, with meaning and applications.
- electric circuits – Why does have a shunt resistance in parallel to a galavanometer decrease the amount of current passing through the galvanometer? – Physics Stack Exchange – discussion with historic “galvanometer”.